Class-02
HTML
The tags that are used in HTML known as a markup, and these tags help the browsers to present the web page structure.
There are two type of markup:
Structural Markup: which are used to describe headings and paragraphs, such as below:
| Structural Markup |
|---|
<h1> - <h6> refers to the heading and subheading |
<p> To create a paragraphs |
<b> <i> To control the characters appearance either bold or italic |
Semantic Markup: which provides extra information for the elements. Here is a list of HTML Semantic elements
The benefits from writing semantic markup are as follows:
- Search engines will consider its contents as important keywords to influence the page’s search rankings.
- Screen readers can use it as a signpost to help visually impaired users navigate a page.
- Finding blocks of meaningful code is significantly easier.
- Suggests to the developer the type of data that will be populated.
-
Semantic naming mirrors proper custom element/component naming.
CSS
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a style sheet language which is used to describe the look and formatting of an HTML elements, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes.
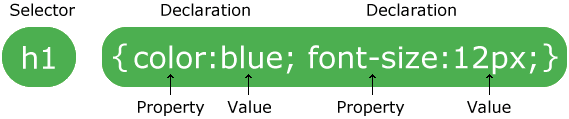
CSS function by linking rules with HTML elements and these rules control how the elements will be displayed. CSS rule consist of two parts:
Selectorwhich describe the element the rule will applies to.Declarationwhich describe the styling that will be used, and it also have two parts:PropertyandValue.
There are three different ways to insert CSS style sheet within the HTML file:
-
External CSSWith an external style sheet. -
Internal CSSAn internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style. -
Inline CSSAn inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
JavaScript
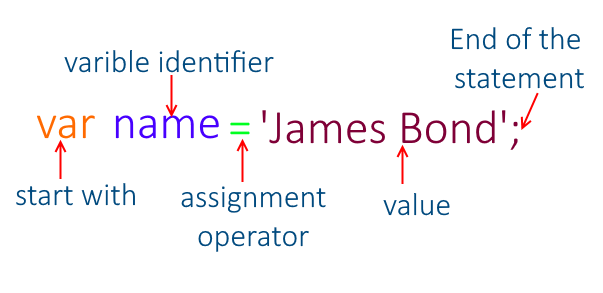
In order to start writing a code in JavaScript we have to declare the variables which perform as a containers for storing data.
JavaScript have different data types that hold different types of values like showed in the table below:
| Data Type |
|---|
1. String : Represents letter, characters and anything between ("Double quotes" & 'Single quotes' |
| 2. Numbers : Represents integer and floating point numbers |
3. Boolean : Represents only two values True and False |
| 4. Undefined : Represents undefined value |
| 5. Null : Represents unknown values |
JavaScript Operators are symbols that are used to perform operations.
Types of Operators:
- Assignment operators: It assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand. The simple assignment operator is equal
=, which assigns the value of its right operand to its left operand. That is,x = yassigns the value ofytox. You could check Assignment Operators to have an overview. - Comparison operators: It compares its operands and returns a logical value based on whether the comparison is true. The operands can be numerical, string, logical, or object values fro example:
x == yorx !== y. You could check Comparison Operators to have an overview. - Arithmetic operators: It takes numerical values (either literals or variables) as their operands and returns a single numerical value for example:
x + y. You could check Arithmetic Operators to have an overview. - Bitwise operators: It treats their operands as a set of 32 bits (zeros and ones), rather than as decimal, hexadecimal, or octal numbers. For example
x >> y. You could check Bitwise Operators to have an overview. - Logical operators: They are typically used with Boolean values; when they are true, they return a Boolean value fro example:
x || yorx && y. You could check Logical Operators to have an overview.